Table of Contents
ToggleCOMPUTER HISTORY:
in the Computer History, Human had desire for using machines for mathematical calculations. One of the most ancient calculating machines was Abacus invented by Chinese about 5000 years ago. after some time man invented faster and more versatile machines to help him in mathematical calculations.
Some notable landmarks in the Computer History are given Below.
-
Pascal’s Adding Machine
- Pascal was a French mathematician, invented a machine in mid of 17th century for adding numbers quickly. It contained a number of gears with the teeth numbered from 0 to 9.
-
Liebniz’s Reckoning Machine
- Pascal’s adding machine was capable of only addition and subtraction. Liebniz, in 1673, improved upon the machine to perform multiplication and division. However, Pascal’s and Liebniz’s machines, because of their complexity, cost and low reliability never became popular.
-
Colmar’s Multiplying Machine
- Colmar, a French scientist, in early nineteenth century, invented a machine similar to Liebniz’s Reckoning Machine that was capable of multiplying numbers quite fast.
-
Babbage’s Difference Engine
- Charles Babbage in 1822 developed a machine known as the difference engine. It could solve differential equations. It had memory to store data and results.
-
Babbage’s Analytical Engine
- Charles Babbage in 1833 improved his machine and named it as “Analytical Engine”. It was capable of all basic arithmetic operations and comparisons. It was based upon the concept of central processor, input, output, memory, etc. It also had the capability to change values already stored in memory.
‘Babbage’ is known as the father of modern computer, because of lack of technology, Babbage ideas were not implemented totally.
Read Also ⇒ Basic Information of Computer
First Computer :
In the Computer History, Dr Howard Aiken of Harvard University, in association with IBM in 1944, constructed an electro-mechanical machine capable of processing a series of instructions in the form of a program. It was named Mark-I. This is considered to be first operational computer.
The Mark-I was a big size machine, Size about- 15.24Mtr. long & 2.44Mtr. having high & comprising more than 750000 parts. It could complete one arithmetic operation on 23 digit numbers in around 03 second.
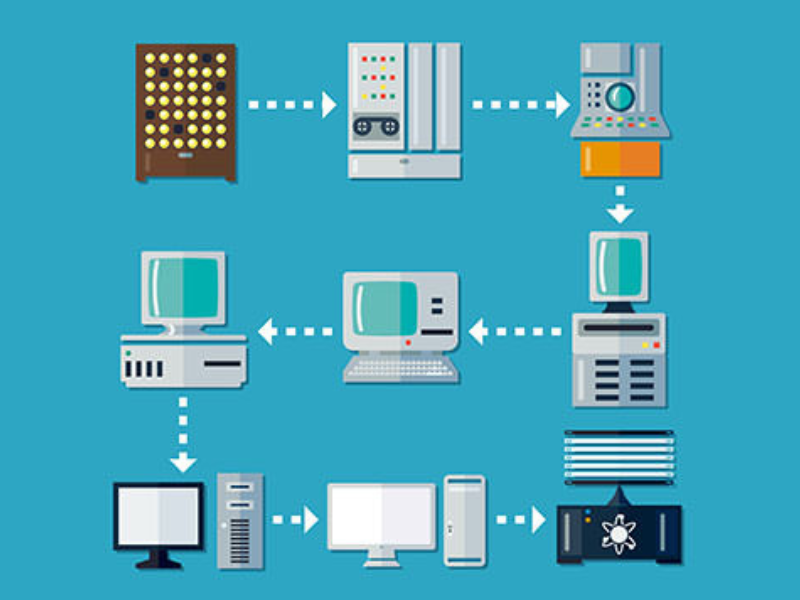
GENERATION OF COMPUTERS :
Since Dr. Howard Aiken constructed the first computer in 1944, the size of computers has decreased & speed capacity and reliability have increased many folds with the passage of time.
Some notable landmarks in technology responsible for this development are given below.
- Invention of transistors
- Invention of integrated circuits
- Development of microprocessors
Before the invention of transistors, the computers used vacuum tubes. The vacuum tubes were bulky and had very low reliability. Invention of transistors, IC and microprocessors contributed to faster and faster computers. Depending upon the technology used, the computers were classified as under.
- First Generation Computers
- Second Generation Computers
- Third Generation Computers
- Fourth Generation Computers
- Fifth Generation Computers
First Generation Computers (1946-1955) :
In the Computer History, The First generation Computer was based upon the thermic valve technology. such computers were very large in size. The reliability of vacuum tubes was also very low. These computers had no operating system and machine language instruction was required for interacting with them .Because of vacuum tubes replacing mechanical devices, the response time was much smaller.
Professor Neumann in 1946 suggested the concept of storing programs in computer memory along with data. This allowed easy manipulation of data using loops in programs. The first computer, based on this principle, was designed in Cambridge University, UK in 1949 by a group of experts headed by Professor Maurice Wilkes. This computer was named Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator (EDSAC).
The IBM 650 was another first generation computer by the IBM Corporation.
The first generation computers generally used stored programs. These programs had to be written in machine language.
Second Generation Computer (1955-1965) :-
In 1947, Bardeen and Brattain invented the transistor that could be used as substitutes for vacuum tubes. These transistors were much more reliable as compared to vacuum tubes since they had no filaments to burn. They were much smaller in size and required very little power. The response time of transistors is also much less as compared to vacuum tubes.
the transistors had the following advantages.
- Reduction in size of the computer
- Reduction in power consumption
- Higher reliability
- Reduction in computation time
- Cost Reduction
In Second Generation Computer, magnetic core was used as the primary memory and magnetic disk as the secondary memory. Magnetic cores are rings with diameters of the order of 0.508 mm made of magnetic material that can be magnetized either in clock-wise or anti-clockwise direction.
Program writing also became easier with the development of high level languages I.e. FORTRAN and COBOL Higher reliability, large memory and decrease in cost led to commercial production of computers.
The IBM 700 and the IBM 1401 series of computers were the popular second generation computers. These were used for commercial applications in industry.
Third Generation Computer (1965-1975) :-
- In mid nineteen sixties, the transistors gave way to Integrated Circuits (IC’s). An IC is an extremely thin wafer of highly purified silicon crystals. A single IC contains all elements of an electronic circuit including transistors, resistors and capacitors along with the leads.
The IBM 360 and the CDC-1700 were popular Third Generation Computers.
Main features of the Third Generation Computers are given below.
- IC-based technology
- Smaller in size
- Less computation time
- Low power consumption
- High reliability
- suitable for commercial applications
- Operating system for users’ interaction
- Multi-tasking environment
- Commercial production at low cost
Fourth Generation Computer (1976-1998) :-
In the Computer History, Use of microprocessor chips in mid seventies marked the advent of Fourth Generation Computers. Medium to very large scale integrated circuits (MSI and VLSI) technology packed about 100000 transistors in a chip. The Intel Corporation in 1971 packed the complete CPU in a single chip. This was known as a microprocessor. This led to production of very powerful personal computers.
Main features of Fourth Generation Computers are given below :-
- Microprocessor-based technology
- Semiconductor memory
- Very small in size
- Highly reliable
- High speed
- Efficient operating system
- Low cost of production
The above features are responsible for the development of very powerful personal computers for use in offices and homes. Another significant development of this period is the graphic devices. This has significantly contributed to use of computers in design, drawing, commercial arts and entertainment.
During the period after 1980, efforts have been put into the system to increase the memory, hard disk capacity and secondary storage.
Microprocessors like Pentium have been used in personal computers to provide speed.
Hard disks of capacity 40 GB are being used for storage of data and application programs.
Optical storage devices CD ROM can store about 600 MB on a 133.35 mm disk.
DVD ROM can store data up to 17 GB. Networking of computers and wide spread use of the Internet contributed to use of computers for communication.
Fifth Generation Computers (1998 onwards) :
Efforts have been put in to increase the reliability, speed, and also decrease power consumption, size and cost of computers. The same trend may continue in future. Some recent developments in silicon technology have generated enthusiasm amongst researchers to develop computers with artificial intelligence and expert systems.
These computers will have thinking power too. Parallel efforts are on to design computers that can understand human voice and interact with users in natural language. Such computers, known as the Fifth Generation Computers.
TYPES OF COMPUTERS :
Computers can be classified into 03 categories :-
- Digital Computer
- Analog Computer
- Hybrid Computer
A. Digital Computer :-
A Digital Computer deals with digital data that can be stored in binary format. Binary data are made of two digits 0 and 1.
According to size and performance, further digital computer may be classified into the following categories:-
- Micro computer
- Mini computer
- Mainframe Computer
- super computer
- Microcomputer
1.Micro Computer :-
A Microcomputer is one whose CPU is a microprocessor. The progress in the field of microcomputers has been phenomenal. From Intel 8088 chip in 1980 it has changed to Intel 80286, 80386, 80486 and Pentium. Microcomputers are used by engineers, business executives and commercial artists. These are also used in homes as personal computers.
The word size of a microcomputer is 8 to 32.
2.Minicomputer :-
A Minicomputer possesses greater amount of memory and storage capacity as compared to microcomputers. The word length of minicomputer is 32 or more. Minicomputers are usually used as multiple-user systems where a large number of people can work together.
The PDP and the VAX are popular minicomputer.
3.Mainframe Computer :-
Mainframe computer is a large and powerful system with a Large Capacity of memory & storage space. power of PC’s has increased tremendously and they are much cheaper, the work that was done earlier by mainframes is being done by PC. Now days mainframes work as nodes for large computer networks. word length of mainframe computers is generally 64.
CDC 6600 and CYBER 170 are popular mainframe computer.
4. Supercomputer :-
Supercomputer consists of a number of processors that can process a variety of jobs in parallel. These are applied mainly for high tech applications like nuclear research. military application, space exploration etc.
PARAM and the ANURAG are supercomputers manufactured in India.
B. Analog Computer :-
Digital computers convert continuous data into digital signals for processing. This process of conversion is known as encoding or digitizing. A digital computer essentially based upon the principle of counting a measurable quantity. However ,an ana log computer can measure a quantity & process it without the need of any digitization.
Such computers are used mainly in scientific applications.
C. Hybrid Computer :-
A computer that can deal with the numeric data and analog signals is known as a hybrid computer.